Ladle
Ladle applications involve the handling, transportation, and refining of molten metal in steelmaking processes. Ladles, lined with high-performance refractory materials, are used to transfer molten steel from the furnace to the tundish or casting mold. They are also employed for processes like alloying, desulfurization, and temperature adjustment to meet specific metallurgical requirements.
In steel plants, ladle applications ensure efficient molten metal management while maintaining its temperature and purity. The use of durable refractory linings prevents heat loss and contamination, enhancing steel quality and production efficiency. Ladles play a vital role in achieving consistent and high-quality steel output.
Slide Gate Plate
Slide gate plates are crucial components used in the steelmaking process to control the flow of molten metal from the ladle to the tundish or mold. Made from high-performance refractory materials, these plates are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. They operate as part of a slide gate system, where their movement helps regulate the molten metal flow, ensuring precision and safety during casting.
In steel plants, slide gate plates play a vital role in maintaining the quality and consistency of molten metal by controlling flow rates and preventing metal oxidation. Their durability and resistance to wear extend the life of the gating system, reduce maintenance requirements, and improve overall casting efficiency. Slide gate plates are essential for enhancing the precision and reliability of the continuous casting process.
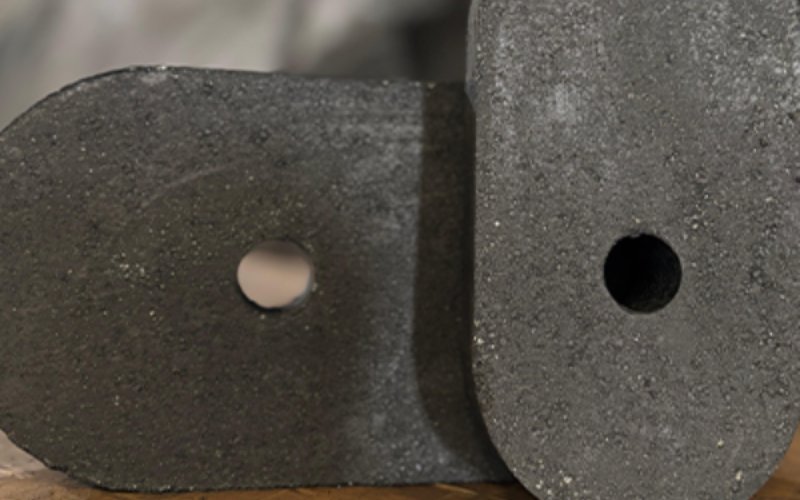


Collector Nozzles
Collector nozzles are critical components in the steelmaking process, used to direct the flow of molten metal from the ladle or tundish into the mold during continuous casting. Made from high-performance refractory materials like alumina or zirconia, these nozzles are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion. They ensure precise control over the flow rate of molten metal, which is essential for producing high-quality steel products.
In steel plants, collector nozzles help optimize the metal flow, reduce defects in casting, and prevent oxidation. Their durability and ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions extend the life of the casting equipment, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. By ensuring smooth and controlled metal flow, collector nozzles contribute significantly to improving casting efficiency, metal quality, and overall production reliability.
Ladle Nozzles
Ladle nozzles are essential refractory components used in steelmaking to control the flow of molten metal from the ladle to the tundish or mold. Made from high-quality refractory materials like alumina or zirconia, these nozzles are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and corrosion caused by molten steel and slag. Ladle nozzles ensure precise and controlled metal flow, which is crucial for high-quality steel production.
In steel plants, ladle nozzles help in regulating the flow of molten metal, reducing oxidation, and maintaining the desired temperature and composition of the steel. Their durability and resistance to extend the lifespan of ladle systems, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. By improving the flow control, ladle nozzles contribute to consistent casting quality, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of steel plants.
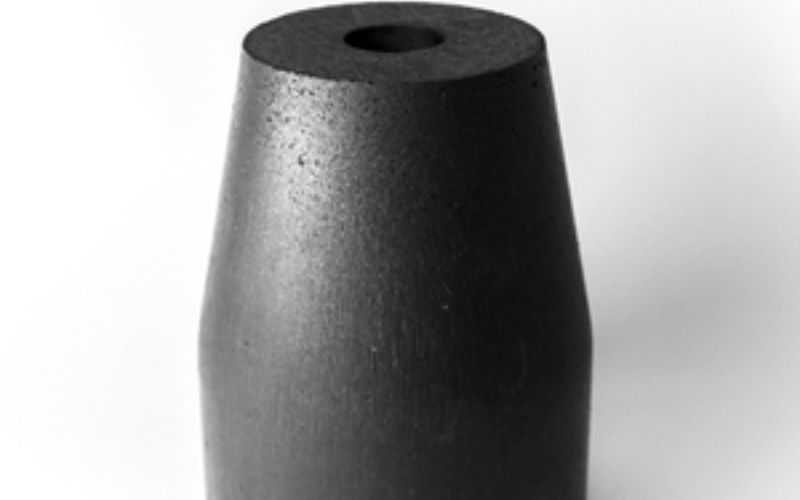
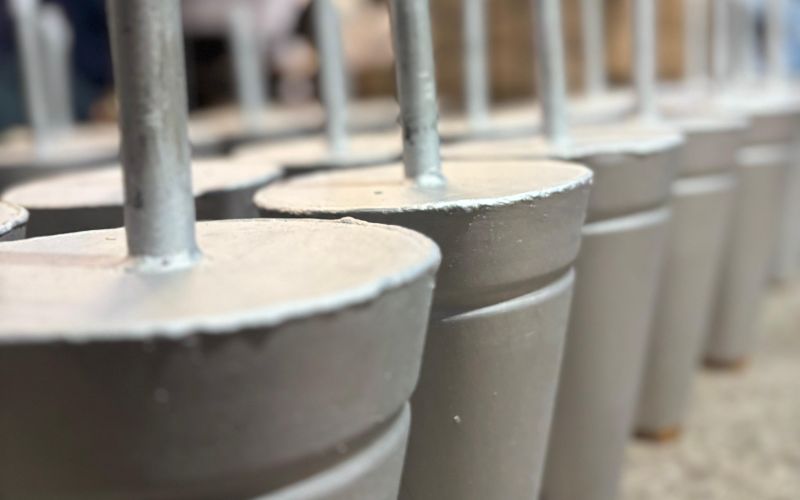


PPGP
Porous plug GP are advanced refractory components used in the steelmaking process to regulate the flow of molten metal in ladles and tundishes. These plugs are designed with specific porosity levels to allow controlled gas injection and precise metal flow, helping maintain the desired composition and temperature of the molten metal. Porous plug GP are typically used in continuous casting processes to improve the efficiency and quality of steel production.
In steel plants, Porous plug GP play a key role in controlling the metal flow, preventing oxidation, and enhancing the refining process through the controlled injection of gases. Their durable, high-performance design ensures resistance to thermal shock, erosion, and corrosion, significantly extending the service life of ladle and tundish systems. By optimizing flow control, Porous plug GP contribute to the overall productivity, safety, and quality of steel manufacturing operations.
PPGP Well Block
PPGP well blocks are specialized refractory components used in the steelmaking process, particularly in the tundish, to form the well area where molten metal accumulates before flowing into the casting nozzle. Made from high-performance refractory materials, PPGP well blocks are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical wear from molten metal and slag. They are specifically engineered for use in high-demand casting applications.
In steel plants, PPGP well blocks are crucial for ensuring smooth metal flow, preventing leaks, and maintaining the overall structural integrity of the tundish. Their high durability and thermal insulation properties help maintain optimal operating conditions and extend the life of the tundish. By ensuring efficient metal flow and minimizing contamination, PPGP well blocks play a vital role in improving the quality of the cast metal and supporting high-quality steel production.
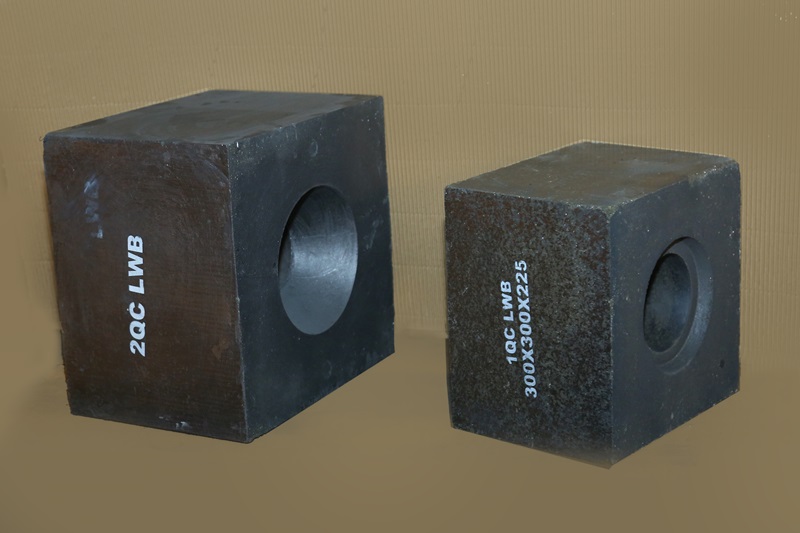
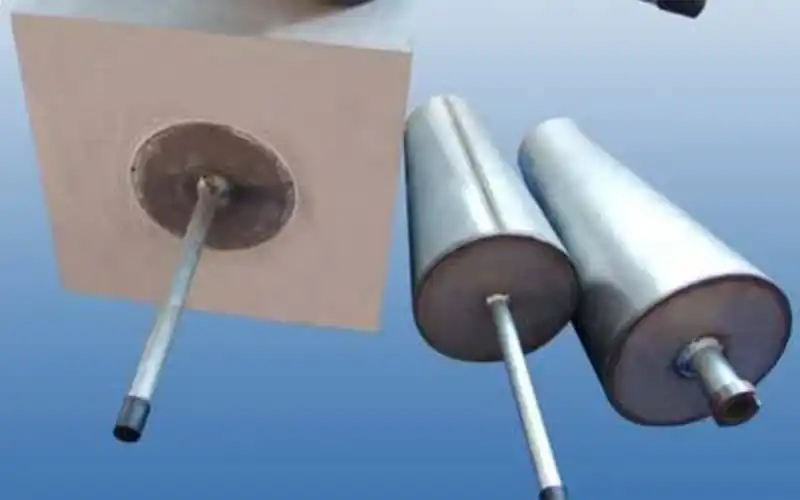

Ladle Well Block
Ladle well blocks are critical refractory components used in the steelmaking process to form the well area in the ladle, where molten metal is collected before it is poured into the tundish or mold. These well blocks are made from high-performance refractory materials, designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical erosion caused by molten steel and slag. They ensure that the molten metal remains contained and flows efficiently.
In steel plants, ladle well blocks are essential for controlling the metal flow, preventing leakage, and improving the efficiency of the casting process. Their durability and resistance to wear extend the service life of ladles and reduce maintenance costs. By providing reliable thermal insulation and protecting the ladle structure, ladle well blocks help ensure smooth operations and high-quality steel production, contributing to the overall productivity of steel plants.
Nozzle Filing Compound
Nozzle filling compound is a specialized refractory material used in steelmaking to fill the gaps and cavities in nozzles, such as ladle and tundish nozzles, to ensure proper functioning and prevent leakage during the molten metal transfer. Made from a mixture of high-temperature resistant materials, it is designed to withstand the extreme conditions inside the nozzle, including high thermal shock and chemical erosion. The compound is applied to create a tight seal and prevent metal spillage or contamination.
In steel plants, nozzle filling compounds are critical for enhancing the performance of the casting process. They improve the sealing of nozzles, ensure smooth molten metal flow, and reduce oxidation or impurities in the metal. These compounds also help extend the service life of nozzles and other related components, reduce downtime for maintenance, and enhance the overall efficiency of steel production.
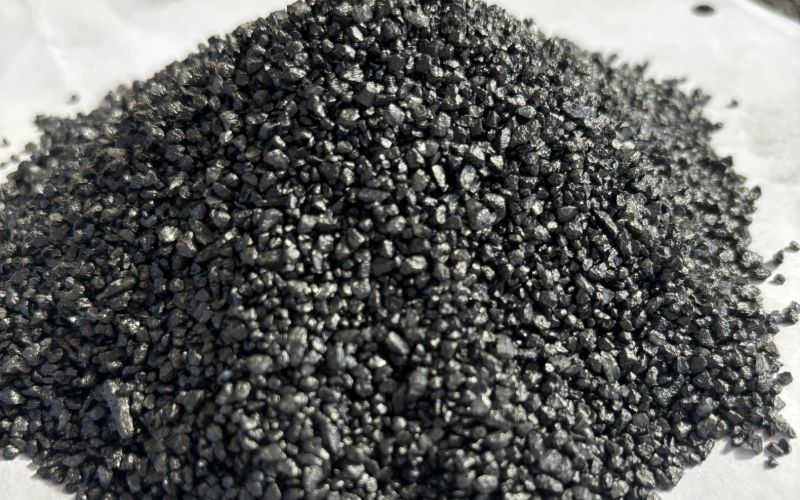
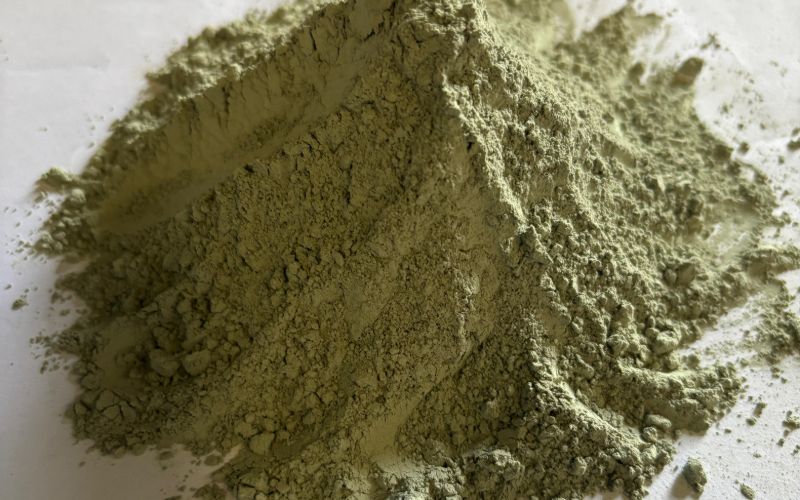


Mortar
Mortar in the context of steelmaking and refractory applications is a specialized mixture used to bond and seal refractory bricks, castables, and other components within high-temperature equipment such as furnaces, kilns, and ladles. It is typically composed of a binder, such as calcium aluminate or silica, and aggregates that provide thermal stability and resistance to heat, corrosion, and mechanical stress. Mortar helps maintain the structural integrity of the refractory lining by filling joints, preventing leaks, and providing additional strength.
In steel plants, mortar plays a crucial role in ensuring the durability and performance of refractory linings. It helps maintain optimal thermal insulation, reduces wear, and extends the service life of high-temperature equipment. Mortar also contributes to the efficiency of processes like melting, heating, and refining by improving heat retention and minimizing heat loss, which is vital for energy conservation and consistent production quality.
Refractory Castable
Refractory castable is a type of high-performance, heat-resistant material used in the construction and repair of high-temperature industrial equipment, such as furnaces, kilns, ladles, and reactors. Castables are typically made from a mixture of refractory aggregates, bonding agents, and additives that, when mixed with water, can be poured, molded, or applied as a monolithic lining. They are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, making them ideal for use in steelmaking, cement, and other high-heat industrial processes.
In steel plants, refractory castables are crucial for lining furnaces, ladles, and tundishes, providing excellent thermal insulation, structural integrity, and protection from molten metal and slag. Castables are highly durable and versatile, ensuring long service life and reducing maintenance downtime. They also contribute to energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss, optimizing temperature control, and maintaining stable thermal conditions in high-temperature applications.
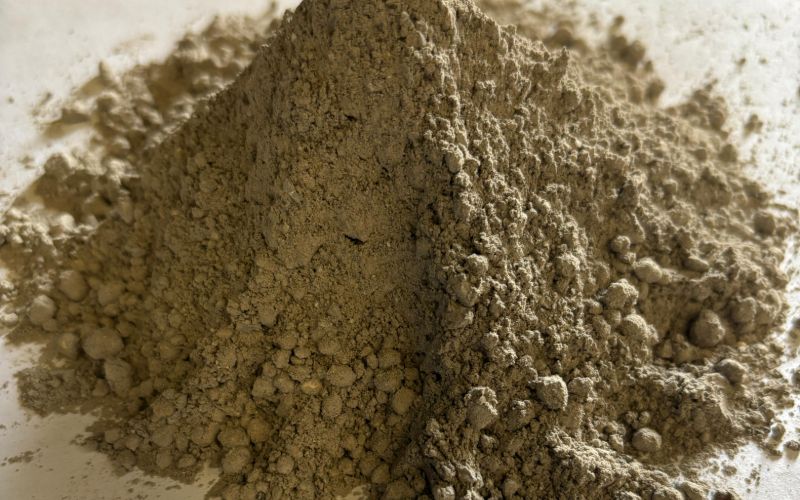
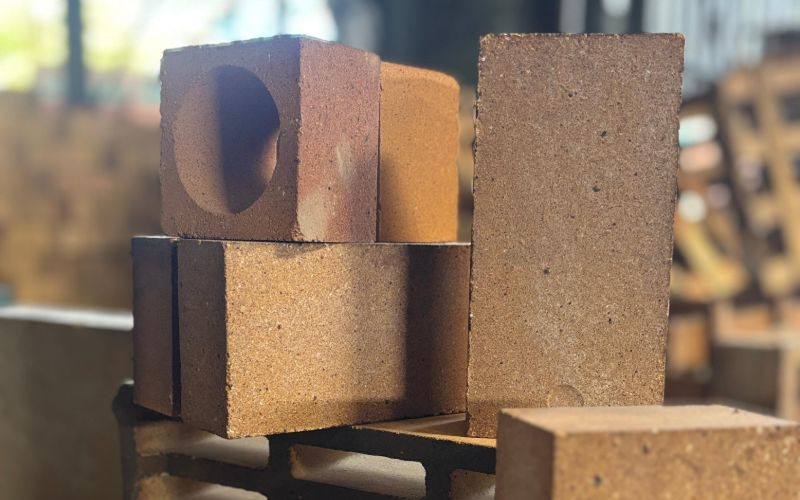


Bricks
Refractory bricks are heat-resistant materials used to line high-temperature industrial equipment such as furnaces, kilns, reactors, and ladles. Made from materials like alumina, silica, or magnesia, these bricks are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical erosion from molten metal, slag, and gases. Their primary function is to provide thermal insulation and structural support while protecting the equipment from high-temperature environments.
In steelmaking and other industries, refractory bricks are critical for maintaining the efficiency and durability of furnaces and other high-temperature processes. They help retain heat, reduce energy loss, and improve temperature control, ensuring consistent and high-quality production. Refractory bricks also extend the lifespan of equipment by preventing wear and corrosion, reducing maintenance costs, and enhancing the overall productivity of industrial operations.
Radex
Radex is a type of advanced refractory material commonly used in high-temperature industrial applications, including steelmaking, to provide excellent protection against thermal shock, corrosion, and erosion. Radex is typically used for lining furnaces, ladles, and other high-heat equipment. It is formulated to offer superior performance in environments exposed to molten metals, slag, and intense heat.
In the steel industry, Radex is valued for its durability and ability to maintain its structural integrity under extreme conditions. It helps reduce wear on equipment, enhance heat retention, and improve overall energy efficiency. The material’s resistance to thermal cycling and its ability to withstand the abrasive effects of molten metal contribute to extending the service life of critical components, thereby reducing maintenance and downtime. Radex is commonly used to ensure high-quality steel production by optimizing the performance and longevity of industrial systems.


All Mechanical Items
In the context of steelmaking and high-temperature industrial applications, mechanical items refer to the various mechanical components used for operation, maintenance, and control within furnaces, ladles, tundishes, and other equipment. These components are critical for ensuring smooth and efficient operations in steel plants and other industrial processes. Some common mechanical items in such environments include:
- Lifting Mechanisms
- Slide Gate Systems
- Hydraulic Systems
- Nozzle Holders and Plates
- Pump Systems
- Heat Exchangers
- Gating Systems
- Transport Systems
- Valves and Actuators
- CI Plug and etc.